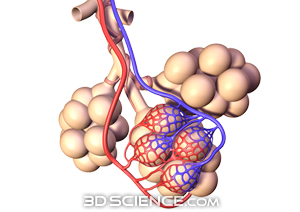
The human heart is about the size of a clenched fist. It contains four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. Oxygen-poor blood enters the right atrium through a major vein called the vena cava. The blood passes through the tricuspid valveinto the right ventricle. Next, the blood is pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs for gas exchange. Oxygen-rich blood returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein. The oxygen-rich blood flows through the bicuspid (mitral) valve into the left ventricle, from which it is pumped through a major artery, the aorta to the rest of the body. . Two valves called semilunar valves are found in the pulmonary artery and aorta.The heart then pumps blood again to the rest of the body to supply oxygen to the cells and collect carbon dioxide to be delivered to the lungs for removal.